If you've not heard of scabies until now, you're not alone. At any given time, some 200 million people worldwide suffer from scabies, yet many of us can go a lifetime without being affected. Let's delve into this tiny yet hugely troublesome skin condition that is causing discomfort across the globe. 🌍

What is scabies?
Scabies is a parasitic infestation caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. These minuscule mites burrow into the skin, lay eggs, and trigger intense itching and a characteristic papular rash.
How do you catch scabies?
Scabies is highly contagious. Here are the ways that you can become infested with scabies.
- Skin-to-Skin Contact: The primary mode of transmission is direct, prolonged skin-to-skin contact (around 20 minutes) with an infested person. Casual contact (like a handshake or hug) is less likely to spread it.
- Sexual Contact: In adults, scabies often spreads through sexual contact.
- Shared Items: Indirect transmission can occur by sharing items like towels, sheets, blankets, pillows, or clothes with an infected person.
- Crowded Settings: Scabies can spread more easily in crowded places such as child care centers, nursing homes, and prisons.
What effects does scabies cause?
Scabies isn’t just an annoyance; it can lead to serious complications:
-
Intense Itch: The hallmark symptom, often worse at night.
-
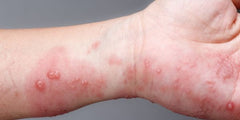
Linear Burrows and Papules: These itchy lines and bumps appear on fingers, wrists, arms, legs, and belt areas.
-
Crusted (Norwegian) Scabies: A severe form with thousands of mites, causing dry, scaly skin. It’s life-threatening and highly contagious.
-
Secondary Bacterial Infections: Scratching can lead to skin sores and bacterial infections.
-
Kidney Disease Risk: Outbreaks of scabies are linked to acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis.
So you may be wondering, how to I get rid of scabies in my home, or avoid catching scabies when I stay at accommodation? Or, if you already have the misfortunate of being infested by these mites, you'll want to know how to eliminate them from your body and ease the itching and rash.
While scabies are not visible to the naked eye, their impact can be significant.
How to prevent scabies at home
Wash sheets regularly in hot water.
Regularly vacuum your mattress and surrounding area.
Spray a linen spray that contains neem oil and other repelling oils.
Help! I need to eliminate scabies at home
Scabies can contaminate various parts of the home. Consider cleaning all such items as:
- Bedding
- Couches
- Chairs
- Car seats
- Carpets and rugs
- Pillows
- Bedding
- Blankets
- Towels
Wash Clothing and Linens: Clean all clothes, towels, and bedding used within three days before the treatment. Use hot, soapy water for washing. Dry items at high heat. If you can’t wash certain items at home, consider dry cleaning them.
Vacuum the mattress and surrounding area to remove any mites or eggs.
Starve the Mites: Seal infested clothing in a plastic bag. This helps eliminate mites.
Treat Family Members: Even if asymptomatic, everyone living in the same household as an infested person should be treated. Preventing re-infection is crucial.
How long can scabies live in bedding?
Scabies mites can survive outside the human body for up to 2 to 3 days.How can I prevent scabies when staying at a hotel or accommodation

When staying at a hotel, preventing scabies involves taking a few precautions to minimise the risk of exposure:
Avoid Close Contact: Limit direct skin-to-skin contact with other guests or hotel staff. Scabies spreads through prolonged contact, so maintain a safe distance.Avoid Shared Items: Avoid using shared towels, blankets, or pillows that may have been used by previous guests. Bring your own where possible.
How to treat scabies
Firstly, always consult with a healthcare provider to have the scabies diagnosed and for a treatment plan. As mentioned, this can be a serious disease so it needs to be treated carefully. Our advice given here is for information and is not medical advice.
Please remember that treating all household contacts simultaneously is crucial to prevent re-infestation.
Treatment options:
-
Topical Medications: Permethrin Cream is widely used. There are some natural treatments to consider to complement medical treatments and offer relief - but, again, if you think you have scabies, please seek professional medical advice.
-
Oral Medication: especially if the patient’s immune system is compromised.
How long does it take for scabies to go away?
- Typical Scabies: With proper treatment, typical scabies usually resolves within 2 to 4 weeks.
- Severity and Immune System: The duration depends on factors such as the severity of infestation and the patient’s immune system. Some people are allergic to the dead mites and eggs and can contiue to experience itching.
- Treatment Effectiveness: If the treatment is effective, you should notice improvement within a few weeks.
- Multiple Treatments: Some individuals may need two or three treatments to completely eliminate the mites.
How to soothe scabies affected skin
Natural Remedies:

- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and acaricidal properties, tea tree oil relieves itching and heals skin rashes caused by scabies. Not effective against deeper-lying eggs.
- Neem Oil: Has antibacterial properties and can kill scabies mites.
- Aloe Vera: Soothes and treats scabies effectively.
- Cayenne Pepper: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Clove Oil: Offers relief from itching.
Remember to consult with a healthcare provider before using any remedies, especially if you’re pregnant, breastfeeding, or have medical concerns. While natural options can provide relief, they should complement professional advice and treatment.
Scabies may be small, but its impact is significant. By understanding its symptoms, causes, and preventive measures, we can combat this global itch together. Remember, early detection and proper treatment are key to keeping scabies at bay!
Disclaimer: Always consult a healthcare professional for personalised advice and treatment.
1: World Health Organization (WHO) 2: Healthdirect Australia






























